
A Community-led Recovery: ARPA Funds in Central Falls, RI
A group started VOCES CON PODER in Central Falls, RI, to use participatory democracy practices to allocate ARPA funds in their community.

A group started VOCES CON PODER in Central Falls, RI, to use participatory democracy practices to allocate ARPA funds in their community.

Youth Voice Youth Vote PB (YV2 PB) was launched in Oregon in 2022 to use participatory democracy practices to allocate ARPA funds.
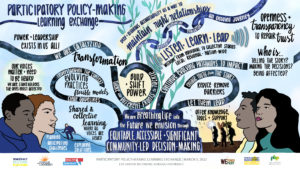
This graphic presents a vision for participatory policy-making rooted in equity, accessibility, and significance. It’s the result of a learning exchange event the Democracy Beyond Elections coalition convened.

This toolkit uses the umbrella term “participatory democracy” to refer to processes that put real decision-making power in community hands, such as ballot initiatives, policy juries or assemblies, and participatory policy-making.

This brief offers considerations for making virtual decision-making processes accessible and equitable throughout and beyond the COVID-19 era. It also highlights several platforms and tools used to facilitate digital engagement and participation.

This booklet provides information on how your community can and must have a say in American Rescue Plan Fund Allocation.

This one-pager gives an overview of what Democracy Beyond Elections (DBE) is providing goals and solutions to deepen participatory democracy.
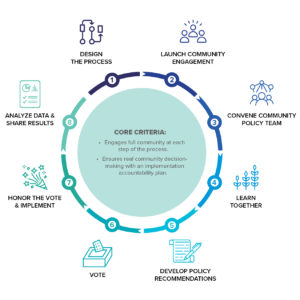
This one-pager gives an overview of what participatory policy-making (PPM) is, why it is a useful tool, the working group that developed the PPM model, and an overview of the steps in the process.

In 2018, the New York City Department of Housing Preservation and Development (HPD) and the New York City Housing Authority (NYCHA) collaborated with dozens of other government agencies, community-based partners, and consultants to launch “Where We Live NYC.”

When Alderman Carlos Ramirez-Rosa took office in 2015, he initiated a six-month long process to restructure the way zoning and development decisions were made in Chicago’s 35th Ward.
We must ensure that the decisions reached by community-led decision-making processes are taken seriously, honored, and implemented transparently. Community-led decision-making processes should hold real tangible value — not be relegated to trivial and theoretical exercises. They should have power over significant budgets or policies. True participatory democracy requires that committees or councils are not just “surveys” to gauge attitudes and views – followed by a business as usual process where people already in power go behind closed doors to make the final decision. In order to be transformational, community-led decision-making processes must have teeth and transparency — from beginning to end, including implementation.
We must equip community members with the tools, knowledge, and information they need to meaningfully participate. It is not enough to say that everyone can participate. We must create the conditions in our processes that make it so everyone can participate. This means community-led decision making processes that provide and center access needs including but not limited to language access, disability access, and economic access. This requires us to ensure that processes are built with community so that they take into account the access to technology, meeting times and locations, and even modes of communication that work for the particular community. Barriers to participation like age, citizenship, registering to vote, location, should be directly addressed and removed.
We must ensure that if you live in the community, you have a role and a voice in how decisions are made – and in making them. Unlike traditional elections, which are filled with barriers to participation, community-led decision making centers directly impacted community members.
Participatory democracy requires that folks left out of traditional election-centered democracy, including but not limited to Black communities, immigrants, and formerly and currently incarcerated folks, are centered in both the leadership of participatory practices and their outcomes.
We must ensure that community-led decision-making processes center and serve the needs of most impacted communities — from outreach, participation, and voice, through to implementation.